pw_presubmit#
The presubmit module provides Python tools for running presubmit checks and
checking and fixing code format. It also includes the presubmit check script for
the Pigweed repository, pigweed_presubmit.py.
Presubmit checks are essential tools, but they take work to set up, and
projects don’t always get around to it. The pw_presubmit module provides
tools for setting up high quality presubmit checks for any project. We use this
framework to run Pigweed’s presubmit on our workstations and in our automated
building tools.
The pw_presubmit module also includes pw format, a tool that provides a
unified interface for automatically formatting code in a variety of languages.
With pw format, you can format Bazel, C, C++, Python, GN, and Go code
according to configurations defined by your project. pw format leverages
existing tools like clang-format, and it’s simple to add support for new
languages. (Note: Bazel formatting requires buildifier to be present on your
system. If it’s not Bazel formatting passes without checking.)
The pw_presubmit package includes presubmit checks that can be used with any
project. These checks include:
Check code format of several languages including C, C++, and Python
Initialize a Python environment
Run all Python tests
Run pylint
Run mypy
Ensure source files are included in the GN and Bazel builds
Build and run all tests with GN
Build and run all tests with Bazel
Ensure all header files contain
#pragma once
Compatibility#
Pigweed AI summary: Python 3 is mentioned in the Compatibility section.
Python 3
Creating a presubmit check for your project#
Creating a presubmit check for a project using pw_presubmit is simple, but
requires some customization. Projects must define their own presubmit check
Python script that uses the pw_presubmit package.
A project’s presubmit script can be registered as a
pw_cli plugin, so that it can be run as pw
presubmit.
Setting up the command-line interface#
The pw_presubmit.cli module sets up the command-line interface for a
presubmit script. This defines a standard set of arguments for invoking
presubmit checks. Its use is optional, but recommended.
Common pw presubmit command line arguments#
Pigweed AI summary: This document outlines the command line arguments for the "pw presubmit" tool, which is used to run checks on code changes before they are submitted. The tool can be run with various options, including specifying paths or patterns to restrict the checks, excluding certain paths using regular expressions, and running actions for all files instead of just changed files. Other options include running the tool in dry-run mode, continuing running presubmit steps after a failure, and specifying a seed for random number generators. The
usage: pw presubmit [-h] [-b commit | --all] [-e regular_expression]
[--dry-run] [-k] [--continue-after-build-error]
[--rng-seed RNG_SEED]
[--output-directory OUTPUT_DIRECTORY]
[--package-root PACKAGE_ROOT] [--clear]
[pathspec [pathspec ...]]
Positional Arguments#
Pigweed AI summary: This section discusses positional arguments, specifically the "pathspec" option which allows for restricting checks to specific paths or patterns interpreted as Git pathspecs. If the "--base" option is used, only changes since that commit will be checked.
- pathspec
Paths or patterns to which to restrict the checks. These are interpreted as Git pathspecs. If –base is provided, only paths changed since that commit are checked.
Named Arguments#
Pigweed AI summary: This paragraph describes the various named arguments that can be used with Git's presubmit command. These arguments include specifying a Git revision to diff against, running actions for all files instead of just changed files, excluding certain paths using regular expressions, executing the presubmit in dry-run mode, continuing running presubmit steps after a failure, setting a seed for random number generators, specifying an output directory and package root directory, and deleting the presubmit output directory. Default values are also provided for
- -b, --base
Git revision against which to diff for changed files. Default is the tracking branch of the current branch: @{upstream}
Default: “@{upstream}”
- --all, --full
Run actions for all files, not just changed files.
- -e, --exclude
Exclude paths matching any of these regular expressions, which are interpreted relative to each Git repository’s root.
Default: []
- --dry-run
Execute the presubits with in dry-run mode. System commands thatpw_presubmit would run are instead printed to the terminal.
- -k, --keep-going
Continue running presubmit steps after a failure.
- --continue-after-build-error
Within presubmit steps, continue running build steps after a failure.
- --rng-seed
Seed for random number generators.
Default: 1
- --output-directory
Output directory (default: <repo root>/out/presubmit)
- --package-root
Package root directory (default: <env directory>/packages)
- --clear, --clean
Delete the presubmit output directory and exit.
pw_presubmit.cli Python API#
Argument parsing code for presubmit checks.
- pw_presubmit.cli.add_arguments(parser: ArgumentParser, programs: Optional[Programs] = None, default: str = '') None#
Adds common presubmit check options to an argument parser.
- pw_presubmit.cli.run(default_program: Optional[Program], program: Sequence[Program], step: Sequence[Check], substep: str, output_directory: Optional[Path], package_root: Path, clear: bool, root: Optional[Path] = None, repositories: Collection[Path] = (), only_list_steps=False, list_steps: Optional[Callable[[], None]] = None, dry_run: bool = False, **other_args) int#
Processes arguments from add_arguments and runs the presubmit.
- Parameters:
default_program – program to use if neither –program nor –step is used
program – from the –program option
step – from the –step option
substep – from the –substep option
output_directory – from –output-directory option
package_root – from –package-root option
clear – from the –clear option
root – base path from which to run presubmit checks; defaults to the root of the current directory’s repository
repositories – roots of Git repositories on which to run presubmit checks; defaults to the root of the current directory’s repository
only_list_steps – list the steps that would be executed, one per line, instead of executing them
list_steps – list the steps that would be executed with their docstrings
**other_args – remaining arguments defined by by add_arguments
- Returns:
exit code for sys.exit; 0 if successful, 1 if an error occurred
Presubmit output directory#
Pigweed AI summary: The pw_presubmit command line interface has an option called --output-directory that sets the working directory for presubmits. The default path is out/presubmit and a subdirectory is created for each presubmit step. This directory can be cleaned by deleting it or running pw presubmit --clean.
The pw_presubmit command line interface includes an --output-directory
option that specifies the working directory to use for presubmits. The default
path is out/presubmit. A subdirectory is created for each presubmit step.
This directory persists between presubmit runs and can be cleaned by deleting it
or running pw presubmit --clean.
Presubmit checks#
A presubmit check is defined as a function or other callable. The function must
accept one argument: a PresubmitContext, which provides the paths on which
to run. Presubmit checks communicate failure by raising an exception.
Presubmit checks may use the filter_paths decorator to automatically filter
the paths list for file types they care about.
Either of these functions could be used as presubmit checks:
@pw_presubmit.filter_paths(endswith='.py')
def file_contains_ni(ctx: PresubmitContext):
for path in ctx.paths:
with open(path) as file:
contents = file.read()
if 'ni' not in contents and 'nee' not in contents:
raise PresumitFailure('Files must say "ni"!', path=path)
def run_the_build(_):
subprocess.run(['make', 'release'], check=True)
Presubmit checks functions are grouped into “programs” – a named series of
checks. Projects may find it helpful to have programs for different purposes,
such as a quick program for local use and a full program for automated use. The
example script uses pw_presubmit.Programs to define
quick and full programs.
PresubmitContext has the following members:
root: Source checkout root directoryrepos: Repositories (top-level and submodules) processed bypw presubmitoutput_dir: Output directory for this specific presubmit stepfailure_summary_log: File path where steps should write a brief summary of any failurespaths: Modified files for the presubmit step to check (often used in formatting steps but ignored in compile steps)all_paths: All files in the repository tree.package_root: Root directory forpw packageinstallationsoverride_gn_args: Additional GN args processed bybuild.gn_gen()luci: Information about the LUCI build or None if not running in LUCInum_jobs: Number of jobs to run in parallelcontinue_after_build_error: For steps that compile, don’t exit on the first compilation errorrng_seed: Seed from--rng-seedor 1, for the few steps that need to seed a random number generator
The luci member is of type LuciContext and has the following members:
buildbucket_id: The globally-unique buildbucket id of the buildbuild_number: The builder-specific incrementing build number, if configured for this builderproject: The LUCI project under which this build is running (oftenpigweedorpigweed-internal)bucket: The LUCI bucket under which this build is running (often ends withciortry)builder: The builder being runswarming_server: The swarming server on which this build is runningswarming_task_id: The swarming task id of this buildcas_instance: The CAS instance accessible from this buildpipeline: Information about the build pipeline, if applicable.triggers: Information about triggering commits, if applicable.
The pipeline member, if present, is of type LuciPipeline and has the
following members:
round: The zero-indexed round number.builds_from_previous_iteration: A list of the buildbucket ids from the previous round, if any, encoded as strs.
The triggers member is a sequence of LuciTrigger objects, which have the
following members:
number: The number of the change in Gerrit.patchset: The number of the patchset of the change.remote: The full URL of the remote.project: The name of the project in Gerrit.branch: The name of the branch on which this change is being/was submitted.ref: Therefs/changes/..path that can be used to reference the patch for unsubmitted changes and the hash for submitted changes.gerrit_name: The name of the googlesource.com Gerrit host.submitted: Whether the change has been submitted or is still pending.
Additional members can be added by subclassing PresubmitContext and
Presubmit. Then override Presubmit._create_presubmit_context() to
return the subclass of PresubmitContext. Finally, add
presubmit_class=PresubmitSubClass when calling cli.run().
Substeps#
Pigweed AI summary: This section explains how presubmit steps can define substeps that can run independently in other tooling. These substeps should subclass "SubStepCheck" and define a "substeps()" method that yields "SubStep" objects. These objects have a name, substep code, positional arguments, and keyword arguments. The "SubStep" objects must have unique names. An example of a "SubStepCheck" subclass is provided in "GnGenNinja" in "build.py".
Presubmit steps can define substeps that can run independently in other tooling.
These steps should subclass SubStepCheck and must define a substeps()
method that yields SubStep objects. SubStep objects have the following
members:
name: Name of the substep_func: Substep codeargs: Positional arguments for_funckwargs: Keyword arguments for_func
SubStep objects must have unique names. For a detailed example of a
SubStepCheck subclass see GnGenNinja in build.py.
Existing Presubmit Checks#
Pigweed AI summary: This document outlines various presubmit checks available in Pigweed, a collection of embedded development libraries. These checks include code formatting, sorted blocks, .gitmodules, #pragma once, TODO formatting, Python checks, inclusive language, OWNERS files, JSON files, and source in build checks. The document provides details on how to include these checks in a presubmit program and how to configure options for each check.
A small number of presubmit checks are made available through pw_presubmit
modules.
Code Formatting#
Pigweed AI summary: The Pigweed project offers formatting checks for various programming languages, including C/C++, Java, Go, Python, GN, and others. These checks can be added to a presubmit program using pw_presubmit.format_code.presubmit_checks(). The checks use language-specific formatters like clang-format or black and suggest fixes using pw format --fix. Options for code formatting can be specified in the pigweed.json file, including the choice of Python formatter, the executable to use for black, the
Formatting checks for a variety of languages are available from
pw_presubmit.format_code. These include C/C++, Java, Go, Python, GN, and
others. All of these checks can be included by adding
pw_presubmit.format_code.presubmit_checks() to a presubmit program. These
all use language-specific formatters like clang-format or black.
These will suggest fixes using pw format --fix.
Options for code formatting can be specified in the pigweed.json file
(see also SEED-0101). These apply to both pw presubmit
steps that check code formatting and pw format commands that either check
or fix code formatting.
python_formatter: Choice of Python formatter. Options areblack(used by Pigweed itself) andyapf(the default).black_path: Ifpython_formatterisblack, use this as the executable instead ofblack.black_config_file: Set the config file for the black formatter.exclude: List of path regular expressions to ignore. Will be evaluated against paths relative to the checkout root usingre.search.
Example section from a pigweed.json file:
{
"pw": {
"pw_presubmit": {
"format": {
"python_formatter": "black",
"black_config_file": "$pw_env{PW_PROJECT_ROOT}/config/.black.toml"
"black_path": "black",
"exclude": [
"\\bthird_party/foo/src"
]
}
}
}
}
Sorted Blocks#
Pigweed AI summary: This section explains how to keep blocks of code in sorted order using comments in Python. The comments include options for case-insensitive sorting, allowing duplicates, ignoring prefixes, and disabling inline comments. The presubmit program can suggest fixes and future versions may support additional multiline list items.
Blocks of code can be required to be kept in sorted order using comments like the following:
# keep-sorted: start
bar
baz
foo
# keep-sorted: end
This can be included by adding pw_presubmit.keep_sorted.presubmit_check to a
presubmit program. Adding ignore-case to the start line will use
case-insensitive sorting.
By default, duplicates will be removed. Lines that are identical except in case
are preserved, even with ignore-case. To allow duplicates, add
allow-dupes to the start line.
Prefixes can be ignored by adding ignore-prefix= followed by a
comma-separated list of prefixes. The list below will be kept in this order.
Neither commas nor whitespace are supported in prefixes.
# keep-sorted: start ignore-prefix=',"
'bar',
"baz",
'foo',
# keep-sorted: end
Inline comments are assumed to be associated with the following line. For
example, the following is already sorted. This can be disabled with
sticky-comments=no.
# keep-sorted: start
# TODO(b/1234) Fix this.
bar,
# TODO(b/5678) Also fix this.
foo,
# keep-sorted: end
By default, the prefix of the keep-sorted line is assumed to be the comment
marker used by any inline comments. This can be overridden by adding lines like
sticky-comments=%,# to the start line.
Lines indented more than the preceding line are assumed to be continuations. Thus, the following block is already sorted. keep-sorted blocks can not be nested, so there’s no ability to add a keep-sorted block for the sub-items.
# keep-sorted: start
* abc
* xyz
* uvw
* def
# keep-sorted: end
The presubmit check will suggest fixes using pw keep-sorted --fix.
Future versions may support additional multiline list items.
.gitmodules#
Pigweed AI summary: This section describes the rules that can be applied to .gitmodules files. These rules can be included in a presubmit program using the pw_presubmit.gitmodules.create() function, which takes an optional argument of type pw_presubmit.gitmodules.Config. The Config object has several properties, including allow_submodules, allow_non_googlesource_hosts, allowed_googlesource_hosts, require_relative_urls, allow_sso, allow_git_corp_google_com, require_branch, and validator
Various rules can be applied to .gitmodules files. This check can be included
by adding pw_presubmit.gitmodules.create() to a presubmit program. This
function takes an optional argument of type pw_presubmit.gitmodules.Config.
Config objects have several properties.
allow_submodules: bool = True— If false, don’t allow any submodules.allow_non_googlesource_hosts: bool = False— If false, all submodule URLs must be on a Google-managed Gerrit server.allowed_googlesource_hosts: Sequence[str] = ()— If set, any Google-managed Gerrit URLs for submodules most be in this list. Entries should be likepigweedforpigweed-review.googlesource.com.require_relative_urls: bool = False— If true, all submodules must be relative to the superproject remote.allow_sso: bool = True— If false,sso://andrpc://submodule URLs are prohibited.allow_git_corp_google_com: bool = True— If false,git.corp.google.comsubmodule URLs are prohibited.require_branch: bool = False— If true, all submodules must reference a branch.validator: Callable[[PresubmitContext, Path, str, Dict[str, str]], None] = None— A function that can be used for arbitrary submodule validation. It’s called with thePresubmitContext, the path to the.gitmodulesfile, the name of the current submodule, and the properties of the current submodule.
#pragma once#
Pigweed AI summary: The article discusses the use of #pragma once in C/C++ headers and how a pragma_once check can be enabled by adding pw_presubmit.cpp_checks.pragma_once to a presubmit program.
There’s a pragma_once check that confirms the first non-comment line of
C/C++ headers is #pragma once. This is enabled by adding
pw_presubmit.cpp_checks.pragma_once to a presubmit program.
TODO(b/###) Formatting#
Pigweed AI summary: This section discusses the formatting of TODO lines in code. The preferred format is "TODO: b/### - Explanation", but projects can define their own pattern. Older formats are still allowed but discouraged. The allowed formats are listed in a code block. To use this check, add "todo_check.create(todo_check.BUGS_OR_USERNAMES)" to a presubmit program.
There’s a check that confirms TODO lines match a given format. Upstream
Pigweed expects these to look like TODO: b/### - Explanation, but makes it
easy for projects to define their own pattern instead.
Some older forms are still allowed but discouraged. In order of preference we allow the following formats by default.
# TODO: b/1234 - Explanation.
# TODO: username@ - Explanation.
# TODO: username@example.com - Explanation.
# TODO(b/1234): Explanation.
# TODO(username) Explanation.
To use this check add todo_check.create(todo_check.BUGS_OR_USERNAMES) to a
presubmit program.
Python Checks#
Pigweed AI summary: The pw_presubmit.python_checks module contains two checks: gn_pylint and gn_python_check. These checks require a top-level python GN target. Gn_pylint runs Pylint and Mypy checks, while gn_python_check runs Pylint, Mypy, and all Python tests.
There are two checks in the pw_presubmit.python_checks module, gn_pylint
and gn_python_check. They assume there’s a top-level python GN target.
gn_pylint runs Pylint and Mypy checks and gn_python_check runs Pylint,
Mypy, and all Python tests.
Inclusive Language#
Pigweed AI summary: The inclusive language check is designed to identify non-inclusive language in code, such as using "master" and "slave" instead of "primary" and "secondary" or "sanity check" instead of "consistency check." It can be disabled for individual lines or entire blocks using specific commands.
The inclusive language check looks for words that are typical of non-inclusive code, like using “master” and “slave” in place of “primary” and “secondary” or “sanity check” in place of “consistency check”.
These checks can be disabled for individual lines with “inclusive-language: ignore” on the line in question or the line above it, or for entire blocks by using “inclusive-language: disable” before the block and “inclusive-language: enable” after the block.
OWNERS#
Pigweed AI summary: The article discusses a presubmit check that requires specific folders to contain "OWNERS" files. The function "module_owners.presubmit_check()" can be added to a presubmit program and takes a callable as an argument to indicate where the controlling "OWNERS" file should be for a given file. The formatting of "OWNERS" files is handled similarly to other source files and is discussed in the "Code Formatting" section.
There’s a check that requires folders matching specific patterns contain
OWNERS files. It can be included by adding
module_owners.presubmit_check() to a presubmit program. This function takes
a callable as an argument that indicates, for a given file, where a controlling
OWNERS file should be, or returns None if no OWNERS file is necessary.
Formatting of OWNERS files is handled similary to formatting of other
source files and is discussed in Code Formatting.
JSON#
Pigweed AI summary: The JSON check ensures that all *.json files are valid JSON files and can be added to a presubmit program by including json_check.presubmit_check().
The JSON check requires all *.json files to be valid JSON files. It can be
included by adding json_check.presubmit_check() to a presubmit program.
Source in Build#
Pigweed AI summary: Pigweed offers checks to ensure that source files are properly configured in the build for GN, Bazel, and CMake. These checks can be added to a presubmit check by including the appropriate functions. The CMake check also requires a callable to invoke CMake with the correct options.
Pigweed provides checks that source files are configured as part of the build
for GN, Bazel, and CMake. These can be included by adding
source_in_build.gn(filter) and similar functions to a presubmit check. The
CMake check additionally requires a callable that invokes CMake with appropriate
options.
pw_presubmit#
The pw_presubmit package provides tools for running presubmit checks.
- class pw_presubmit.FileFilter(*, exclude: Iterable[_StrOrPattern] = (), endswith: Iterable[str] = (), name: Iterable[_StrOrPattern] = (), suffix: Iterable[str] = ())#
Allows checking if a path matches a series of filters.
Positive filters (e.g. the file name matches a regex) and negative filters (path does not match a regular expression) may be applied.
- __init__(*, exclude: Iterable[_StrOrPattern] = (), endswith: Iterable[str] = (), name: Iterable[_StrOrPattern] = (), suffix: Iterable[str] = ()) None#
Creates a FileFilter with the provided filters.
- Parameters:
endswith – True if the end of the path is equal to any of the passed strings
exclude – If any of the passed regular expresion match return False. This overrides and other matches.
name – Regexs to match with file names(pathlib.Path.name). True if the resulting regex matches the entire file name.
suffix – True if final suffix (as determined by pathlib.Path) is matched by any of the passed str.
- matches(path: Union[str, Path]) bool#
Returns true if the path matches any filter but not an exclude.
If no positive filters are specified, any paths that do not match a negative filter are considered to match.
If ‘path’ is a Path object it is rendered as a posix path (i.e. using “/” as the path seperator) before testing with ‘exclude’ and ‘endswith’.
- exception pw_presubmit.PresubmitFailure(description: str = '', path: Optional[Path] = None, line: Optional[int] = None)#
Optional exception to use for presubmit failures.
- __init__(description: str = '', path: Optional[Path] = None, line: Optional[int] = None)#
- class pw_presubmit.Programs(**programs: Sequence)#
A mapping of presubmit check programs.
Use is optional. Helpful when managing multiple presubmit check programs.
- __init__(**programs: Sequence)#
Initializes a name: program mapping from the provided keyword args.
A program is a sequence of presubmit check functions. The sequence may contain nested sequences, which are flattened.
- pw_presubmit.call(*args, call_annotation: Optional[Dict[Any, Any]] = None, **kwargs) None#
Optional subprocess wrapper that causes a PresubmitFailure on errors.
- pw_presubmit.filter_paths(*, endswith: Iterable[str] = (), exclude: Iterable[Union[str, Pattern[str]]] = (), file_filter: Optional[FileFilter] = None, always_run: bool = False) Callable[[Callable], Check]#
Decorator for filtering the paths list for a presubmit check function.
Path filters only apply when the function is used as a presubmit check. Filters are ignored when the functions are called directly. This makes it possible to reuse functions wrapped in @filter_paths in other presubmit checks, potentially with different path filtering rules.
- Parameters:
endswith – str or iterable of path endings to include
exclude – regular expressions of paths to exclude
file_filter – FileFilter used to select files
always_run – Run check even when no files match
- Returns:
a wrapped version of the presubmit function
Git hook#
Pigweed AI summary: This section explains how to use a git hook to run presubmit checks before pushing changes to a remote repository. It is recommended to only run fast and trivial checks as push hooks and perform slower or more complex ones in continuous integration. This is because running slow checks in the push hook can cause longer wait times for git push to complete and if a change fails a check at this stage, it will not yet be uploaded to the remote, making it harder to debug any failures.
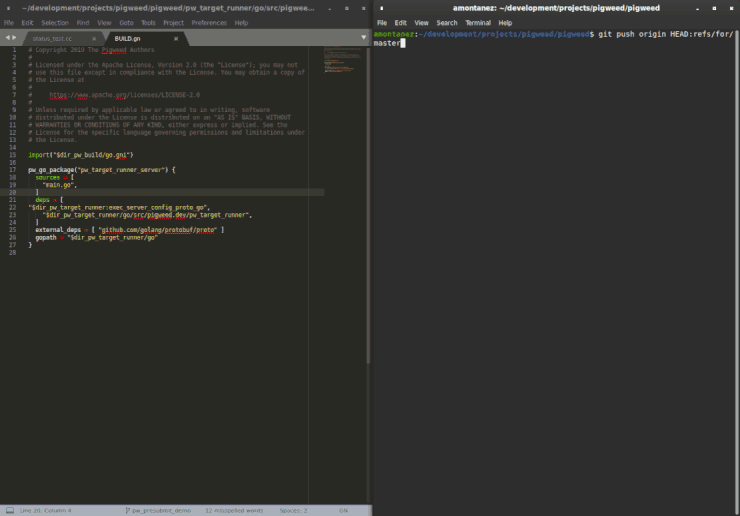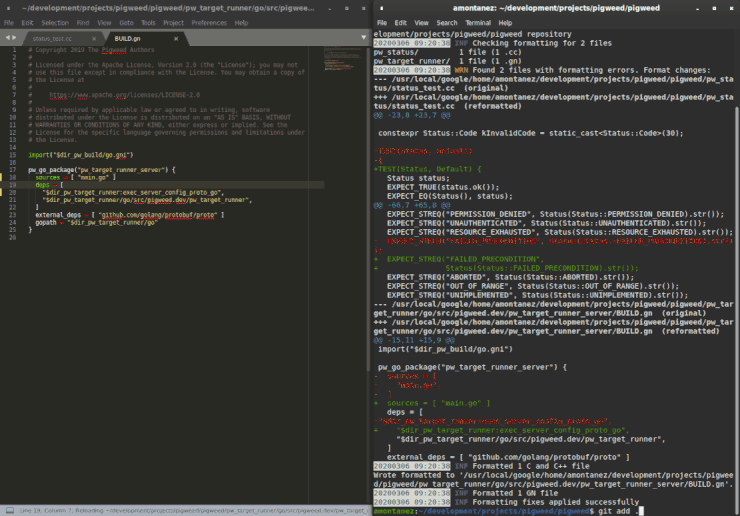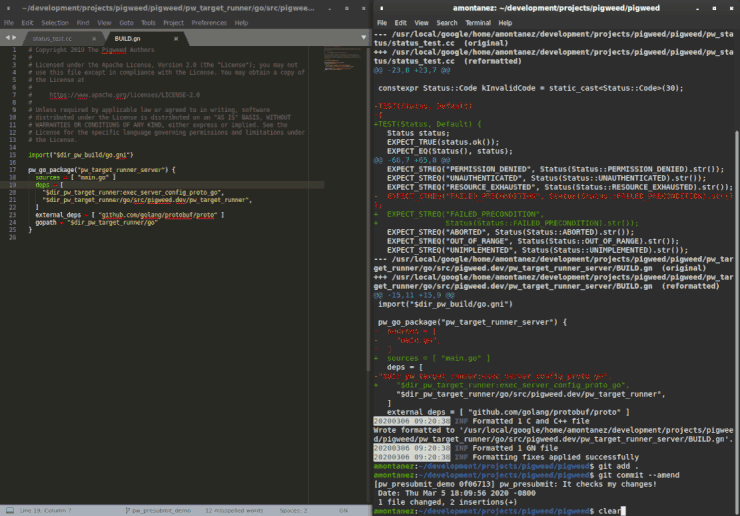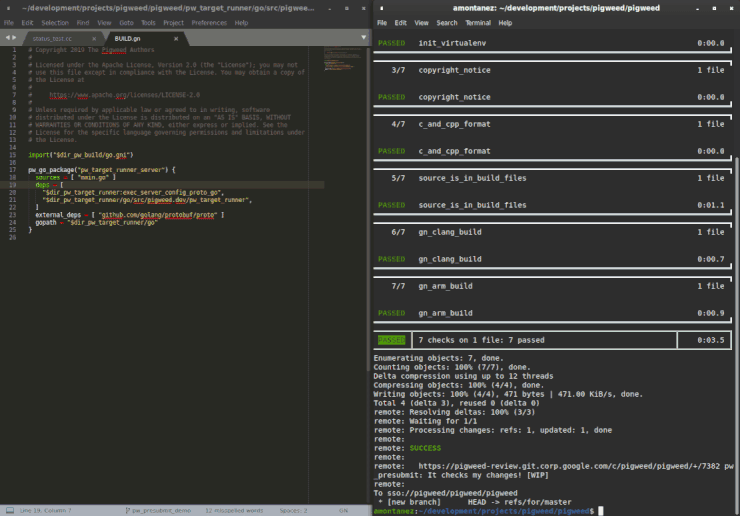
You can run a presubmit program or step as a git hook using
pw_presubmit.install_hook. This can be used to run certain presubmit
checks before a change is pushed to a remote.
We strongly recommend that you only run fast (< 15 seconds) and trivial checks as push hooks, and perform slower or more complex ones in CI. This is because,
Running slow checks in the push hook will force you to wait longer for
git pushto complete, andIf your change fails one of the checks at this stage, it will not yet be uploaded to the remote, so you’ll have a harder time debugging any failures (sharing the change with your colleagues, linking to it from an issue tracker, etc).
Example#
Pigweed AI summary: This is a simple example presubmit check script that can be used as a starting point for a project's presubmit check script. It includes various presubmit checks such as release build, host tests, pragma once, formatting checks, and inclusive language check. The script also allows for the installation of a Git pre-push hook and the passing of a remote ref for use by the pre-push hook.
A simple example presubmit check script follows. This can be copied-and-pasted to serve as a starting point for a project’s presubmit check script.
See pigweed_presubmit.py for a more complex presubmit check script example.
"""Example presubmit check script."""
import argparse
import logging
import os
from pathlib import Path
import re
import sys
from typing import Optional
try:
import pw_cli.log
except ImportError:
print("ERROR: Activate the environment before running presubmits!", file=sys.stderr)
sys.exit(2)
import pw_presubmit
from pw_presubmit import (
build,
cli,
cpp_checks,
format_code,
inclusive_language,
python_checks,
)
from pw_presubmit.presubmit import filter_paths
from pw_presubmit.presubmit_context import PresubmitContext
from pw_presubmit.install_hook import install_git_hook
# Set up variables for key project paths.
PROJECT_ROOT = Path(os.environ["MY_PROJECT_ROOT"])
PIGWEED_ROOT = PROJECT_ROOT / "pigweed"
# Rerun the build if files with these extensions change.
_BUILD_EXTENSIONS = frozenset(
[".rst", ".gn", ".gni", *format_code.C_FORMAT.extensions]
)
#
# Presubmit checks
#
def release_build(ctx: PresubmitContext):
build.gn_gen(ctx, build_type="release")
build.ninja(ctx)
build.gn_check(ctx) # Run after building to check generated files.
def host_tests(ctx: PresubmitContext):
build.gn_gen(ctx, run_host_tests="true")
build.ninja(ctx)
build.gn_check(ctx)
# Avoid running some checks on certain paths.
PATH_EXCLUSIONS = (
re.compile(r"^external/"),
re.compile(r"^vendor/"),
)
# Use the upstream pragma_once check, but apply a different set of path
# filters with @filter_paths.
@filter_paths(endswith=".h", exclude=PATH_EXCLUSIONS)
def pragma_once(ctx: PresubmitContext):
cpp_checks.pragma_once(ctx)
#
# Presubmit check programs
#
OTHER = (
# Checks not ran by default but that should be available. These might
# include tests that are expensive to run or that don't yet pass.
build.gn_gen_check,
)
QUICK = (
# List some presubmit checks to run
pragma_once,
host_tests,
# Use the upstream formatting checks, with custom path filters applied.
format_code.presubmit_checks(exclude=PATH_EXCLUSIONS),
# Include the upstream inclusive language check.
inclusive_language.presubmit_check,
# Include just the lint-related Python checks.
python_checks.gn_python_lint.with_filter(exclude=PATH_EXCLUSIONS),
)
FULL = (
QUICK, # Add all checks from the 'quick' program
release_build,
# Use the upstream Python checks, with custom path filters applied.
# Checks listed multiple times are only run once.
python_checks.gn_python_check.with_filter(exclude=PATH_EXCLUSIONS),
)
PROGRAMS = pw_presubmit.Programs(other=OTHER, quick=QUICK, full=FULL)
#
# Allowlist of remote refs for presubmit. If the remote ref being pushed to
# matches any of these values (with regex matching), then the presubmits
# checks will be run before pushing.
#
PRE_PUSH_REMOTE_REF_ALLOWLIST = ("refs/for/main",)
def run(install: bool, remote_ref: Optional[str], **presubmit_args) -> int:
"""Process the --install argument then invoke pw_presubmit."""
# Install the presubmit Git pre-push hook, if requested.
if install:
# '$remote_ref' will be replaced by the actual value of the remote ref
# at runtime.
install_git_hook(
"pre-push",
[
"python",
"-m",
"tools.presubmit_check",
"--base",
"HEAD~",
"--remote-ref",
"$remote_ref",
],
)
return 0
# Run the checks if either no remote_ref was passed, or if the remote ref
# matches anything in the allowlist.
if remote_ref is None or any(
re.search(pattern, remote_ref)
for pattern in PRE_PUSH_REMOTE_REF_ALLOWLIST
):
return cli.run(root=PROJECT_ROOT, **presubmit_args)
return 0
def main() -> int:
"""Run the presubmit checks for this repository."""
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description=__doc__)
cli.add_arguments(parser, PROGRAMS, "quick")
# Define an option for installing a Git pre-push hook for this script.
parser.add_argument(
"--install",
action="store_true",
help="Install the presubmit as a Git pre-push hook and exit.",
)
# Define an optional flag to pass the remote ref into this script, if it
# is run as a pre-push hook. The destination variable in the parsed args
# will be `remote_ref`, as dashes are replaced with underscores to make
# valid variable names.
parser.add_argument(
"--remote-ref",
default=None,
nargs="?", # Make optional.
help="Remote ref of the push command, for use by the pre-push hook.",
)
return run(**vars(parser.parse_args()))
if __name__ == "__main__":
pw_cli.log.install(logging.INFO)
sys.exit(main())
Code formatting tools#
Pigweed AI summary: This text describes code formatting tools in the PigWeed framework. The pw_presubmit.format_code module can be used to format supported source files using external code format tools. The file format_code.py can be invoked from the command line or from pw as pw format. An example is provided for adding support for a custom format, which involves wrapping the built-in formatter to add a new format, replace a formatter, or remove/disable a PigWeed supplied one. The example code is written in Python
The pw_presubmit.format_code module formats supported source files using
external code format tools. The file format_code.py can be invoked directly
from the command line or from pw as pw format.
Example#
Pigweed AI summary: This code provides an example of how to add support for a custom format in Python. It wraps the built-in formatter to add a new format, which can also be used to replace or remove a PigWeed supplied one. The code includes a function to check and fix formatting for source files in the repository. It also imports presubmit checks and a user-defined check. The main function runs the formatting check and exits the program.
A simple example of adding support for a custom format. This code wraps the built in formatter to add a new format. It could also be used to replace a formatter or remove/disable a PigWeed supplied one.
#!/usr/bin/env python
"""Formats files in repository. """
import logging
import sys
import pw_cli.log
from pw_presubmit import format_code
from your_project import presubmit_checks
from your_project import your_check
YOUR_CODE_FORMAT = CodeFormat('YourFormat',
filter=FileFilter(suffix=('.your', )),
check=your_check.check,
fix=your_check.fix)
CODE_FORMATS = (*format_code.CODE_FORMATS, YOUR_CODE_FORMAT)
def _run(exclude, **kwargs) -> int:
"""Check and fix formatting for source files in the repo."""
return format_code.format_paths_in_repo(exclude=exclude,
code_formats=CODE_FORMATS,
**kwargs)
def main():
return _run(**vars(format_code.arguments(git_paths=True).parse_args()))
if __name__ == '__main__':
pw_cli.log.install(logging.INFO)
sys.exit(main())